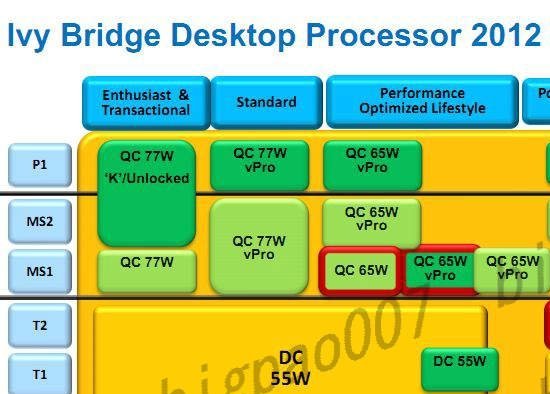
Intel already has the upper hand in energy consumption in the mid-range – and with Ivy Bridge the distance looks to grow. With new 3D transistors and 22 nanometer technology the TDP will be lowered from 95W to 77W.
The processor architecture Ivy Bridge will replace Sandy Bridge in the mid-range in Q2 2012. Besides a more powerful GPU with DirectX 11 support the processor architecture will bring higher IPC (Instructions per cycle), but the perhaps biggest news is still Intel’s fresh 22 nanometer technology and its Tri-gate transistors that Intel has promised will result in substantially better energy efficiency.
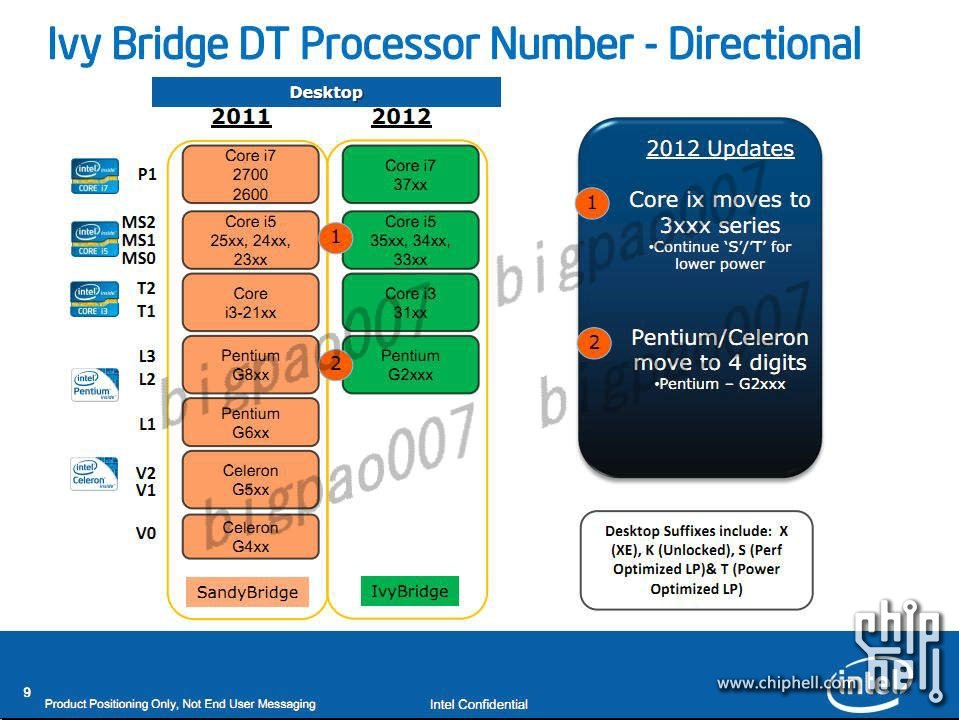
This has been confirmed in leaked specification documents from Intel. The road map first reveal how Intel will revise its product names where Ivy Bridge architecture focuses on four different product series with a number of sub-series;
- Intel Core i7-37xx
- Intel Core i5-35xx/34xx/33xx
- Intel Core i3-31xx
- Intel Pentium G2xxx
Just as with Sandy Bridge, Intel will separate special models with letters at the end; X for extreme models, K for overclocking models, T and S for extra energy efficient models.
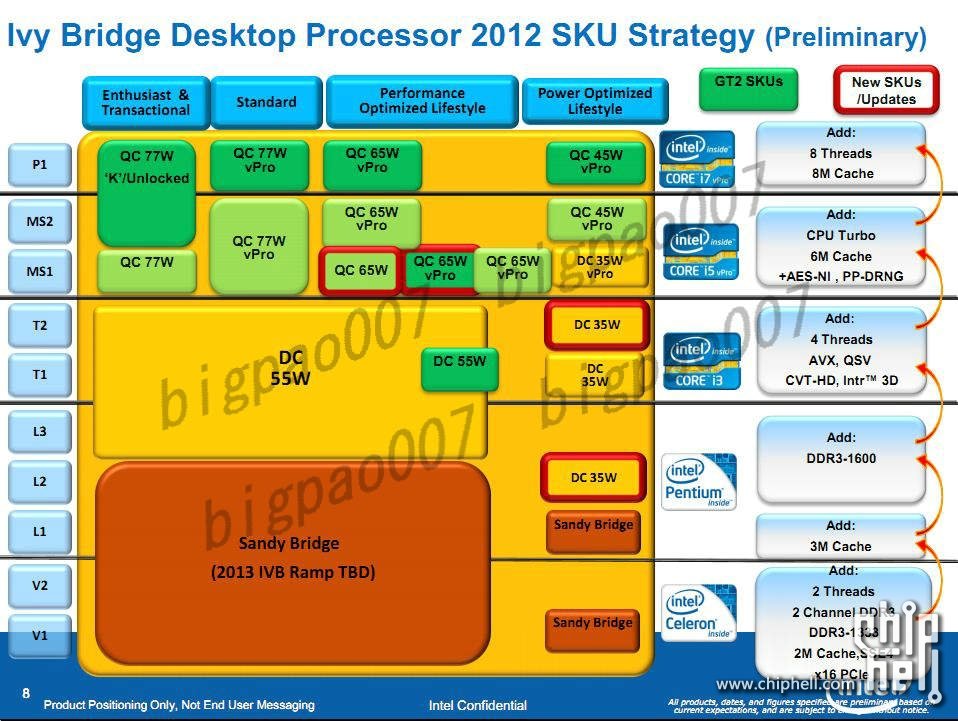
 The energy efficiency is the main attraction of Ivy Bridge and Intel has lowered energy consumption across the board. One more document reveals that not even the K-marked enthusiast models will consume more than 77 watt, which is a reduction of near 20%, despite that the new Core i7-37xx series is expected to offer noticeably better performance over Core i7-26xx series. Intel also plans extra energy efficient models with four cores at 65W, 45W and 35W.
The energy efficiency is the main attraction of Ivy Bridge and Intel has lowered energy consumption across the board. One more document reveals that not even the K-marked enthusiast models will consume more than 77 watt, which is a reduction of near 20%, despite that the new Core i7-37xx series is expected to offer noticeably better performance over Core i7-26xx series. Intel also plans extra energy efficient models with four cores at 65W, 45W and 35W.
If we go to the dual core models of the Core i3-31xx series the TDP starts at 55 watt for the standard models, while the efficient models start at 35 watt.
 Intel will introduce a new standard for energy consumption in its mobile processors. It will will have variable TDPs where the circuits can operate with both higher and lower energies depending on the situation and environment. It has also lowered the energy requirements for the desktop circuits shows an even bigger focus on power saving
Intel will introduce a new standard for energy consumption in its mobile processors. It will will have variable TDPs where the circuits can operate with both higher and lower energies depending on the situation and environment. It has also lowered the energy requirements for the desktop circuits shows an even bigger focus on power saving
Ivy Bridge will according to earlier reports get 20% higher CPU performance and up to 60% higher graphics performance than current Sandy Bridge models. At the same time, energy consumption will be reduced by nearly 20%. Almost too good to be true. The information is unconfirmed, but if true they spell problems ahead for AMD. The recently launched Bulldozer architecture can’t keep with Intel’s top models of the Sandy Bridge program, despte a higher energy consumption on paper.
Intel in turn looks to move from clarity to clarity and during the wait from the for Ivy Bridge we hear good things about the new enthusiast series Sandy Bridge-E waiting around the corner.
Source: ChipHell