Windows 8 is slated for the first half of 2012, bringing support for ARM system processors. ARM processors are not in the same performance range as x86 processor from AMD and Intel, and they usually don’t have several GB of RAM. This is an area Microsoft has worked the hardest on.
The biggest news with Windows 8 is the new Metro interface adjusted for tablets and the support for ARM. According to Qualcomm the next generation ARM circuits should outperform Intel Atom, but they are still no performance processors and will not have several GB of RAM to work with, so getting the requirements down is a key part for Microsoft.
In the latest blog entry it talks about ways of imroving the memory handling. One thing it has changed is background programs and sevices. With Windows 7 many of the services run as Windows Update, Plug and Play constantly in the background and consumes unnecessary memory. With Windows 8 the programs will only run when needed, when the user want them. Without reducing the functionality it will reduce memory usage substantially.
Another imrpovement is that the memory handler can search for duplicates of a file in the memory, erase them and run only one copy. Then the single copy can be used for various programs and services instead of having multiple in the memory. Additionally it allows developers to set parts of the programs to run as low priority. This means that when the operating system needs memory, it can remove the least important bits from the RAM.
 |
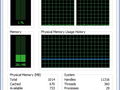 |
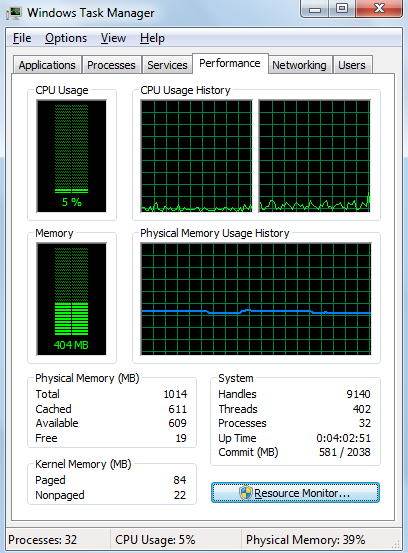
Here it compares Windows 7, against Windows 8, on an old netbook with 1 GB memorym which is the minimum requirement. The difference is substantial with a reduction of memory usage of nearly 31%. We see that the processor usage is down too. Windows 8 looks like a radical improvement over Windows 7, besides the new interface there is loads of optimizations.
Source: Microsoft



















